Ever wonder how the ads you see on google are created? Well, I do. And this blog will provide you with the insights of basic “Google Ads Fundamentals.”
What are Google Ads?
According to “Google Ads Fundamentals” course, it is defined as an “online advertising tool that helps businesses connect with their customers” (Academy for Ads,2017).
You create your online ad, tell Google Ads who you want to reach, and Google Ads brings your ads to them” (Academy for Ads,2017).
Let’s Talk Benefits
- Connect with customers when it matters– It targets the right crowd, at the right time.
- Control your costs– It gives you the ability to have control over your budget and you get to pick how you want to spend your money.
- Improve performance – Google lets you see how your ad is performing by its’ tracking tools that shows you what percentage of people visited your website and actual sales your website is generating as a direct result of your ads.
Where can your customers see your Ads?
Google Ads are split into 2 networks:
- Google Search
- Google Display
Google search networks partners with Google, they include Google Search, Google Shopping, Google Maps, and Google Play. On the other hand, Google Display teams up with partnering websites that aid in similar search results. These sites include YouTube, Blogger, and Gmail (“Academy for Ads”, 2017).
There are multiple formats on the Google Network

Text Ads –
The most common kind of Search ad includes a descriptive headline, website URL, and descriptive text like a call to action.
Ads with Extensions –
Ad extensions provide additional information to your text ad, such as your business’s address or phone number.
Responsive Ads –
The Display Network offers ads that adjust to match the pages and apps that show them. Viewers are more likely to see these ads because they blend in with the content the viewers came for. Responsive ads can go a long way to help build awareness, influence consideration, and drive action.
Shopping Ads –
In addition to an image, Shopping ads contain product and pricing information, so users get a strong sense of the product you’re selling before they click your ad. They’re ideal if you’re managing a large inventory of products.
Image Ads – Image ads capture people’s attention as they browse websites in the Google Display Network.
Video Ads – Video ads are just what they sound like — a standalone video ad or a video ad that runs inside another streaming video.
*Video ads show on search partner networks, but not the Google Search Network.
App Promotion Ads –
App promotion ads send your customers to an app store to download your app, or include a deep link directly into your app.
Call-only Ads –
Call-only ads allow your customers to call your business directly by clicking on your ad. They’re useful for driving phone calls to your business from devices that can make calls.
Rich Media Ads –
Rich media ads are engaging ad formats that often include animation or other types of motion.
Create Effective Texts

Text ads, “The most common kind of Search ad includes a descriptive headline, website URL, and descriptive text (description) like a call to action” (“Academy for Ads”, 2017). To make sure your text ad is effective, make sure to:
Tips on writing the perfect Text Ad:
- Highlight what makes you unique
- Use a call to action
- Include sales terms
- Match the ad to your keywords
- Match the ad to your landing page
Enhance your Ad with Extensions
If you want to grab your audience’s attention, Ad extensions are a good way to do so because it gives individuals more reason to pick you business. And a on the plus side, there is no fee to set up a Ad extension.

Sitelink extension: direct to a specific page of your website (hours).
Callout extension: add additional text.
Structured snippets: highlight specific aspects of your products or services.
Location extension: direct people to physical locations (stores).
Call extension: adding a phone # for people to call.
Message extension: adding a # for people to text.
Price extension: showcase categories with their prices
Promotion extension: highlight specific sales (40% off).
App extension: link to your mobile apps.
Choose the Right Campaign Type
The important part of creating an Ad is knowing your advertising goals and then you can pick the right campaign to achieve it.
Step 1
- Search campaign
- Display campaign
- Search campaigns with display opt-in
- Video campaign
- Shopping campaign
- Universal App campaign
Step 2
- Select objectives for your campaign
Step 3
- Campaign name
- Campaign type Networks (partner sites)
- Devices Locations & Languages
- Bidding
- BudgetAd extensions
A good campaign helps your business make changes quickly, target your ads effectively, and reach your advertising goals as a result.
Organize your Account for Success
A business must have an organized campaign and know the 3 “layers” of Google Ads that will help their business practices (“Academy for Ads”, 2017).


Account: It should be a unique email address and password along with billing information.
Campaign: Have a budget and settings that determine where your ads appear.
Ad Group: It contains a set of similar ads along with keywords (phrases or words that are relevant to your ads).
To keep on the right track, make sure to:
- Create separate campaigns for different areas
- Create separate ad groups with relevant keywords
- Explore Google Ad manager if your juggling multiple accounts
Reach Customers with Targeting
At this point in time, you should have a campaign type and your business objective in mind.
When targeting audience you should think:
WHO – is in your targeted audience?
WHERE– your audience is?
WHAT– is of interest to your audience?
Help Customers Find You
Keywords are a great tool to reach potential or current customers. Because the point of keywords is for your customers to find you easily. Here is how you make them effective:

- Think like a customer when you create a list.
- Organize keywords by them Specific keywords target specific customers
- General keywords attract more people.
- Use negative keywords – that aren’t relevant to your product or service.
- Pick the right number of keywords.
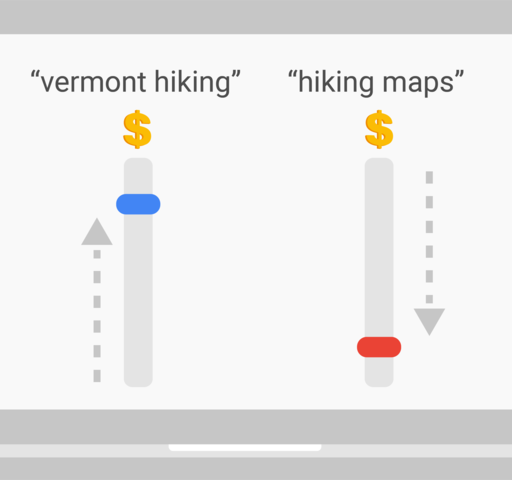
Control Which Searches Trigger your Ads
When customers search for or visit a website with terms in your keyword list they can see your ad. This match is done broadly by default so your ad can show to the largest possible audience (Academy for Ads, 2017).
The Solution is – Match types (which variations of your keywords cause your ad to show).
Broad match – includes all keywords, close variations, synonyms & misspellings.
Setup: leave as default (no changes)
Broad match modifier – same as the broad match but excludes synonyms (more targeted).
Setup: add a plus sign (+) sign before each term (word)
Phrase match – ads based on exact phrases & close variations.
Setup: add quotes(“ ”) around terms
Exact match – ads based on exact keywords & close variations.
Setup: add brackets[ ] around terms
Negative match – prevents ads from showing specific term related to search (excludes those keywords).
Setup: add a minus sign (-) before terms
The impact of ad formats you have enabled, your ad’s expected clickthrough rate (CTR), ad relevancy, and finally, the landing page experience when users click on your ad are all infuential (Academy for Ads, 2017).
Make your Ads Seen

- Google Ads auction – considers what’s relevant & what’s high on Ad Rank.
- Ad Rank– considers the bid amount, expected clickthrough rate (CTR), landing page, ad relevancy & ad formats. All of these factors affect your quality score and determined your ad placement on a certain page (“Academy for Ads”, 2017).
Match media cost models with your budget
Lets talk about the different cost methods for your advertisements.
CPM – Plaster ads all around the internet (pay the same price, regardless if people see it or not). It helps raise brand awareness.
vCPM – Only pay when ads are in visible areas (costs a little more, but people relevant see them). It raises brand awareness but only pay for impressions measured as viewable.
CPC – When someone clicks on your website you pay. It drives traffic to the site.
CPV – Same as CPC, but they watch a video. It increases views of the video.
CPA – Only pay when a customer does something you want them to for example, sign ups or they purchase a product). It helps increase the sales.
Determine a good bidding strategy
Google Ads gives you several ways to bid for your ads. Depending on which networks your campaign is targeting, and whether you want to focus on getting clicks, impressions, or conversions, you can determine which strategy is best for you (Academy for Ads, 2017).
There are two main ways a business can manage their bidding in Google Ads.
- Manual bidding – YOU control the bidding

- Automated bidding – Google Ads controls it for you
Basically, Google Ads direct you to use the “cost-per-click” (CPC) bidding (Academy for Ads, 2017).
Tools to help you determine what to set your CPC, are as follows:
- Bid simulator (“what if” scenarios)
- Keyword Planner (how often your keywords are searched.
- First-page bid estimates (how much you need to spend to be on the first page of results)
Select your bid strategy
Google Ads offers several bid strategies that are targeted to different types of campaigns and business goals. Automated bidding can increase your campaign performance therefore it is the best option (Academy for Ads, 2017).
Ad clicks: Maximize clicks automatically set your bids to help get as many clicks as possible within your budget. It can increase site visits and increase clicks on low-traffic terms
Ad revenue: Target return-on-ad-spend (ROAS) bids more where Google Ads estimates ads are more likely to lead to a sale — aiming to get as much return on ad spend as possible
Ad conversions: Automated bidding strategies designed to generate conversions include Enhanced cost per click (ECPC)Maximize conversions and Target cost per acquisition (CPA)
- ECPC: semi-automated bid strategy that adjusts your bids to get as many conversions as possible within your set budget.
- Maximize conversions: automatic bidding during auction time to get the most conversion volume as possible.
- Target CPA: automatically sets bids to help get as many conversions as possible at the target CPA you set.
Adjust Bids to Favor Performers
What are bid adjustments? According to Academy by Ads, “A bid adjustment allows you to raise or lower your bids in certain scenarios. With bid adjustments, you can bid higher to increase the visibility of your ads” (2017).
Types of bid adjustments include:
Device – Use device bid adjustments to show your ad more or less frequently for searches that occur on different devices.
Location – Use location bid adjustments to show your ad more or less frequently to customers in certain countries, cities, or other geographic areas.
Time of day – Use ad scheduling bid adjustments to increase or decrease your bids on certain days or during certain hours.
Top content – Use bid adjustments for popular content to increase your ad’s chance of showing on top content on YouTube and the Display Network.
Targeting methods – Use bid adjustments for topics, placements, and other targeting methods in campaign types that show ads on the Display Network.
Remarketing lists for search ads – Use bid adjustments for remarketing lists in your ad groups if you’d like to show ads more or less frequently to people on these lists.
Interactions – Use interactions for more control over how potential customers connect with your business.
Align your budget with your goals
How do you determine your daily budget? There are four ways you can calculate your daily budget:
- Calculate based on your monthly budget
- Calculate based on your average cost-per-click
- Find your campaigns recommended budget
- Check your ad delivery method
Evaluate campaign performance
Once your campaign is running, it’s in your best interest to maintain and measure your ad performance (“Academy for Ads”, 2017).
Common questions are asked to evaluate the performance:

The type of report to use for the questions above:
| What searches and site terms have triggered my ad? Search Terms Report Where were the people who triggered my ads? User Locations Report What geographies do my ad viewers care about? Geographic Report Does my landing page need work? Landing Page Experience Report What are the paths that lead people to conversions for my business? Attribution Report |
Another way to measure performance and push results are through metrics:
Impressions – shows how often your ad was shown on a search result page.
Clicks CTR – shows how many clicks your ad has received.
Conversion – show how many people clicked from your ad to your site and did something you valued.
Cost per conversion – shows how much each ad conversion cost you.
Conversion rate – shows how many conversions on your site resulted from an ad click.
Avoid editorial errors
We always proofread our major projects before we submit them so, in the same sense, we have to ensure the quality of our ads. Google policy suggests that, “to ensure a consistent and clear user experience, we enforce quality standards on the ads and the websites advertised on the Google Network” (Academy for Ads, 2017).
Here are some grammar and spelling tips to consider:
- Typos
- Extra punctuation marks e.g., Buy Now!!! or Ready to start???
- Unnecessary use of symbols e.g., &%^*
- Symbols used incorrectly e.g., “+” used to represent “and”
- GiMmIcKy CAPITALIZATI0N and spelling
- Emojis and emoticons
Here are some style tips to consider:
- Don’t include “Click here” in your ad
- Don’t include your phone number in ad text, instead use a Call extension
- Image ads must be clearly branded with things like a company name, logo, and display URL
Conclusion

Google Ads are a very effective way for businesses to reach new and existing customers. After completing the Google Ads Certificate, I have gained quite a bit of knowledge that I can use toward advertising my future business. Not only for myself, I can help other businesses understand the benefit of Google ads and how to use it.
References
Academy for Ads. (2017, September 22). Google Ads Fundamentals. Retrieved from https://academy.exceedlms.com/student/path/3132










